Distance of closest approach of ellipses and ellipsoids
The distance of closest approach of two objects is the distance between their centers when they are externally tangent. The objects may be geometric shapes or physical particles with well defined boundaries. The distance of closest approach is sometimes referred to as the contact distance.
For the simplest objects, spheres, the distance of closest approach is simply the sum of their radii. For non-spherical objects, the distance of closest approach is a function of the orientation of the objects, and its calculation can be difficult. The maximum packing density of hard particles, an important problem of ongoing interest,[1] depends on their distance of closest approach.
The interactions of particles typically depend on their separation, and the distance of closest approach plays an important role in determining the behavior of condensed matter systems.
The excluded volume of particles (the volume excluded to the centers of other particles due to the presence of one) is a key parameter in such descriptions,;[2][3] the distance of closest approach is required to calculate the excluded volume. The excluded volume for identical spheres is just four times the volume of one sphere. For other anisotropic objects, the excluded volume depends on orientation, and its calculation can be surprising difficult.[4] The simplest shapes after spheres are ellipses and ellipsoids; these have received considerable attention,[5] yet their excluded volume is not known. Vieillard Baron was able to provide an overlap criterion for two ellipses. His results were useful for computer simulations of hard particle systems and for packing problems using Monte Carlo simulations.
The one anisotropic shape whose excluded volume can be expressed analytically is the spherocylinder; the solution of this problem is a classic work by Onsager.[6] The problem was tackled by considering the distance between two line segments, which are the center lines of the capped cylinders. Results for other shapes are not readily available. The orientation dependence of the distance of closest approach has surprising consequences. Systems of hard particles, whose interactions are only entropic, can become ordered. Hard spherocylinders form not only orientationally ordered nematic, but also positionally ordered smectic phases.[7] Here, the system gives up some (orientational and even positional) disorder to gain disorder and entropy elsewhere.
Contents |
Distance of closest approach of two ellipses
Vieillard Baron first investigated this problem, although he did not obtain a result for the distance of closest approach, he derived the overlap criterion for two ellipses. His results were useful for the study of the phase behavior of hard particles and for the packing problem using Monte Carlo simulations. Although overlap criteria have been developed,[8][9] analytic solutions for the distance of closest approach and the location of the point of contact have only recently become available.[10][11] The details of the calculations are provided in Ref.[12] The Fortran 90 subroutine is provided in Ref.[13]
The method
The procedure consists of three steps:
- Transformation of the two tangent ellipses
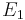 and
and 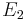 , whose centers are joined by the vector
, whose centers are joined by the vector 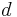 , into a circle
, into a circle 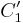 and an ellipse
and an ellipse 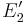 , whose centers are joined by the vector
, whose centers are joined by the vector 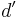 . The circle
. The circle 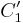 and the ellipse
and the ellipse 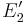 remain tangent after the transformation.
remain tangent after the transformation. - Determination of the distance
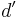 of closest approach of
of closest approach of 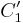 and
and 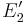 analytically. It requires the appropriate solution of a quartic equation. The normal
analytically. It requires the appropriate solution of a quartic equation. The normal 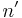 is calculated.
is calculated. - Determination of the distance
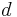 of closest approach and the location of the point of contact of
of closest approach and the location of the point of contact of 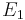 and
and 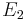 by the inverse transformations of the vectors
by the inverse transformations of the vectors 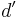 and
and 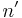 .
.
Input:
- lengths of the semiaxes
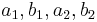 ,
, - unit vectors
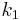 ,
,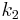 along major axes of both ellipses, and
along major axes of both ellipses, and - unit vector
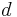 joining the centers of the two ellipses.
joining the centers of the two ellipses.
Output:
- distance
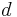 between the centers when the ellipses
between the centers when the ellipses 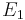 and
and 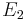 are externally tangent, and
are externally tangent, and - location of point of contact in terms of
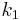 ,
,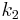 .
.
Distance of closest approach of two ellipsoids
Consider two ellipsoids, each with a given shape and orientation, whose centers are on a line with given direction. We wish to determine the distance between centers when the ellipsoids are in point contact externally. This distance of closest approach is a function of the shapes of the ellipsoids and their orientation. There is no analytic solution for this problem, since solving for the distance requires the solution of a sixth order polynomial equation. Here an algorithm is developed to determine this distance, based on the analytic results for the distance of closest approach of ellipses in 2D, which can be implemented numerically. Details are given in publications.[14][15] Subroutines are provided in two formats: Fortran90 [16] and C.[17]
Method
The algorithm consists of three steps.
- Constructing a plane containing the line joining the centers of the two ellipsoids, and finding the equations of the ellipses formed by the intersection of this plane and the ellipsoids.
- Determining the distance of closest approach of the ellipses; that is the distance between the centers of the ellipses when they are in point contact externally.
- Rotating the plane until the distance of closest approach of the ellipses is a maximum. The distance of closest approach of the ellipsoids is this maximum distance.
References
- ^ S. Torquato and Y. Jiao, Nature 460, 876-879, 2009
- ^ T.L. Hill, An Introduction to Statistical Thermodynamics (Addison Wesley, London, 1960)
- ^ T.A. Witten, and P.A. Pincus, Structured Fluids (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2004)
- ^ Forces, Growth and Form in Soft Condensed Matter: At the Interface between Physics and Biology, ed. A.T. Skjeltrop and A.V. Belushkin, (NATO Science Series II: Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry, 2009),
- ^ A. Donev, F.H. Stillinger, P.M. Chaikin and S. Torquato, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 255506 (2004)
- ^ L. Onsager, Ann NY Acad Sci, 51, 627 (1949)
- ^ D. Frenkel, J. Phys. Chem. 91, 4912-4916 (1987)
- ^ J. Vieillard-Baron, "Phase transition of the classical hard ellipse system" J. Chem. Phys., 56(10), 4729 (1972).
- ^ J. W. Perram and M. S. Wertheim, "Statistical mechanics of hard ellipsoids. I. overlap algorithm and the contact function", J. Comput. Phys., 58, 409 (1985).
- ^ X. Zheng and P. Palffy-Muhoray, "Distance of closest approach of two arbitrary hard ellipses in two dimensions", electronic Liquid Crystal Communications, 2007
- ^ X. Zheng and P. Palffy-Muhoray, "Distance of closest approach of two arbitrary hard ellipses in two dimensions", Phys. Rev. E, 75, 061709 (2007).
- ^ X. Zheng and P. Palffy-Muhoray, Complete version containing contact point algorithm, May 4, 2009.
- ^ Fortran90 subroutine for contact distance and contact point for 2D ellipses by X. Zheng and P. Palffy-Muhoray, May 2009.
- ^ X. Zheng, W. Iglesias, P. Palffy-Muhoray, "Distance of closest approach of two arbitrary hard ellipsoids", Phys. Rev. E, 79, 057702 (2009)
- ^ X. Zheng, W. Iglesias, P. Palffy-Muhoray, "Distance of closest approach of two arbitrary hard ellipsoids", electronic Liquid Crystal Communications, 2008
- ^ Fortran90 subroutine for distance of closest approach of ellipsoids
- ^ C subroutine for distance of closest approach of ellipsoids